1 Defining Teams and Groups
The content included in this chapter is adapted from two Open University chapters: Working in Groups and Teams and Groups and Teamwork
What is a group?
Our tendency to form groups is a pervasive aspect of organizational life. In addition to formal groups, committees, and teams, there are informal groups, cliques, and factions.

Formal groups are used to organize and distribute work, pool information, devise plans, coordinate activities, increase commitment, negotiate, resolve conflicts and conduct inquests. Group work allows the pooling of people’s individual skills and knowledge, and helps compensate for individual deficiencies. Estimates suggest most managers spend 50 percent of their working day in one sort of group or another, and for top management of large organizations this can rise to 80 percent. Thus, formal groups are clearly an integral part of the functioning of an organization.
No less important are informal groups. These are usually structured more around the social needs of people than around the performance of tasks. Informal groups usually serve to satisfy needs of affiliation, and act as a forum for exploring self-concept as a means of gaining support, and so on. However, these informal groups may also have an important effect on formal work tasks, for example by exerting subtle pressures on group members to conform to a particular work rate, or as ‘places’ where news, gossip, etc., is exchanged.
What is a team?
Exploration Activity
Write your own definition of a ‘team’ (in 20 words or less).
Provide an example of a team working toward an achievable goals
You probably described a team as a group of some kind. However, a team is more than just a group. When you think of all the groups that you belong to, you will probably find that very few of them are really teams. Some of them will be family or friendship groups that are formed to meet a wide range of needs such as affection, security, support, esteem, belonging, or identity. Some may be committees whose members represent different interest groups and who meet to discuss their differing perspectives on issues of interest.
In this reading the term ‘work group’ (or ‘group’) is often used interchangeably with the word ‘team,’ although a team may be thought of as a particularly cohesive and purposeful type of work group. We can distinguish work groups or teams from more casual groupings of people by using the following set of criteria (Adair, 1983). A collection of people can be defined as a work group or team if it shows most, if not all, of the following characteristics:
- A definable membership: a collection of three or more people identifiable by name or type;
- A group identity: the members think of themselves as a group;
- A sense of shared purpose: the members share some common task or goals or interests;
- Interdependence: the members need the help of one another to accomplish the purpose for which they joined the group;
- Interaction: the members communicate with one another, influence one another, react to one another;
- Sustainability: the team members periodically review the team’s effectiveness;
- An ability to act together.
Usually, the tasks and goals set by teams cannot be achieved by individuals working alone because of constraints on time and resources, and because few individuals possess all the relevant competences and expertise. Sports teams or orchestras clearly fit these criteria.
Exploration Activity
List some examples of teams of which you are a member – both inside and outside work – in your learning file.
Now list some groups.
What strikes you as the main differences?
By contrast, many groups are much less explicitly focused on an external task. In some instances, the growth and development of the group itself is its primary purpose; process is more important than outcome. Many groups are reasonably fluid and less formally structured than teams. In the case of work groups, an agreed and defined outcome is often regarded as a sufficient basis for effective cooperation and the development of adequate relationships.Teamwork is usually connected with project work and this is a feature of much work. Teamwork is particularly useful when you have to address risky, uncertain, or unfamiliar problems where there is a lot of choice and discretion surrounding the decision to be made. In the area of voluntary and unpaid work, where pay is not an incentive, teamwork can help to motivate support and commitment because it can offer the opportunities to interact socially and learn from others (Piercy & Kramer, 2017). Furthermore, people are more willing to support and defend work they helped create (Stanton, 1992).
Importantly, groups and teams are not distinct entities. Both can be pertinent in personal development as well as organizational development and managing change. In such circumstances, when is it appropriate to embark on teambuilding rather than relying on ordinary group or solo working?
In general, the greater the task uncertainty the more important teamwork is, especially if it is necessary to represent the differing perspectives of concerned parties. In such situations, the facts themselves do not always point to an obvious policy or strategy for innovation, support, and development: decisions are partially based on the opinions and the personal visions of those involved.
There are risks associated with working in teams as well. Under some conditions, teams may produce more conventional, rather than more innovative, responses to problems. The reason for this is that team decisions may regress towards the average, with group pressures to conform cancelling out more innovative decision options (Makin, Cooper, & Cox, 1989). It depends on how innovative the team is, in terms of its membership, its norms, and its values.
Teamwork may also be inappropriate when you want a fast decision. Team decision making is usually slower than individual decision making because of the need for communication and consensus about the decision taken. Despite the business successes of Japanese companies, it is now recognized that promoting a collective organizational identity and responsibility for decisions can sometimes slow down operations significantly, in ways that are not always compensated for by better decision making.
Is a team or group really needed?
There may be times when group working – or simply working alone – is more appropriate and more effective. For example, decision-making in groups and teams is usually slower than individual decision-making because of the need for communication and consensus. In addition, groups and teams may produce conventional rather than innovative responses to problems, because decisions may regress towards the average, with the more innovative decision options being rejected (Makin et al., 1989).
In general, the greater the task uncertainty, that is to say the less obvious and more complex the task to be addressed, the more important it will be to work in a group or team rather than individually. This is because there will be a greater need for different skills and perspectives, especially if it is necessary to represent the different perspectives of the different stakeholders involved.
Table 2 lists some occasions when it will be appropriate to work in teams, in groups or alone.
Table 2
When to work alone, in groups or in teams
| When to work alone or in groups | When to build teams |
| For simple tasks or problems | For highly-complex tasks or problems |
| When cooperation is sufficient | When decisions by consensus are essential |
| When minimum discretion is required | When there is a high level of choice and uncertainty |
| When fast decisions are needed | When high commitment is needed |
| When few competences are required | When a broad range of competences and different skills are required |
| When members’ interests are different or in conflict | When members’ objectives can be brought together towards a common purpose |
| When an organization credits individuals for operational outputs | When an organization rewards team results for strategy and vision building |
| When innovative responses are sought | When balanced views are sought |
Types of teams
Different organizations or organizational settings lead to different types of team. The type of team affects how that team is managed, what the communication needs of the team are and, where appropriate, what aspects of the project the project manager needs to emphasize. A work group or team may be permanent, forming part of the organization’s structure, such as a top management team, or temporary, such as a task force assembled to see through a particular project. Members may work as a group continuously or meet only intermittently. The more direct contact and communication team members have with each other, the more likely they are to function well as a team. Thus, getting a group to function well is a valuable management aim.
The following section defines common types of team. Many teams may not fall clearly into one type, but may combine elements of different types. Many organizations have traditionally been managed through a hierarchical structure. This general structure is illustrated in Figure 1 below.
The number of levels clearly depends upon the size and to some extent on the type of the organization. Typically, the span of control, the number of people each manager or supervisor is directly responsible for, averages about five people, but this can vary widely. As a general rule it is bad practice for any single manager to supervise more than 7-10 people.
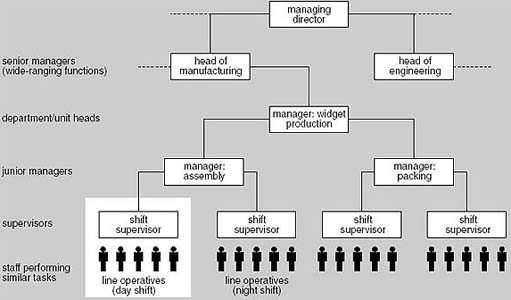
While the hierarchy is designed to provide a stable ‘backbone’ to the organization, projects are primarily concerned with change, and so tend to be organized quite differently. Their structure needs to be more fluid than that of conventional management structures. There are four commonly used types of project team: the functional team, the project (single) team, the matrix team and the contract team.
Exploration Activity
Why is it problematic for a manager to supervise too many people? How does this relate to groups, is there an ideal group size or configuration?
The project (single) team
The hierarchical structure described above divides groups of people along largely functional lines: people working together carry out the same or similar functions. A functional team is a team in which work is carried out within a group organized around a similar function or task. This can be project work. In organizations in which the functional divisions are relatively rigid, project work can be handed from one functional team to another in order to complete the work. For example, work on a new product can pass from marketing, which has the idea, to research and development, which sees whether it is technically feasible, thence to design and finally manufacturing. This is sometimes known as ‘baton passing’ – or, less flatteringly, as ‘throwing it over the wall’!
The project, or single, team consists of a group of people who come together as a distinct organizational unit in order to work on a project or projects. The team is often led by a project manager, though self-managing and self-organizing arrangements are also found. Quite often, a team that has been successful on one project will stay together to work on subsequent projects. This is particularly common where an organization engages repeatedly in projects of a broadly similar nature – for example developing software, or in construction. Perhaps the most important issue in this instance is to develop the collective capability of the team, since this is the currency for continued success. People issues are often crucial in achieving this.
The closeness of the dedicated project team normally reduces communication problems within the team. However, care should be taken to ensure that communications with other stakeholders (senior management, line managers and other members of staff in the departments affected, and so on) are not neglected, as it is easy for ‘us and them’ distinctions to develop.
The matrix team
In a matrix team, staff report to different managers for different aspects of their work. Matrix structures are often, but not exclusively, found in projects. Matrix structures are more common in large and multi-national organizations. In this structure, staff are responsible to the project manager for their work on the project while their functional line manager may be responsible for other aspects of their work such as appraisal, training, and career development, and ‘routine’ tasks. This matrix project structure is represented in Figure 2. Notice how the traditional hierarchy is cross-cut by the ‘automated widget manufacturing configuration.’

In this form of organization, staff from various functional areas (such as design, software development, manufacturing or marketing) are loaned or seconded to work on a particular project. Such staff may work full- or part-time on the project. The project manager thus has a recognizable team and is responsible for controlling and monitoring its work on the project.
However, many of the project staff will still have other duties to perform in their normal functional departments. The functional line managers they report to will retain responsibility for this work and for the professional standards of their work on the project, as well as for their training and career development. It is important to overcome the problems staff might have with the dual reporting lines (the ‘two-boss’ problem). This requires building good interpersonal relationships with the team members and regular, effective communication.
The contract team
The contract team is brought in from outside in order to do the project work. Here, the responsibility to deliver the project rests very firmly with the project manager. The client will find such a team harder to control directly. On the other hand, it is the client who will judge the success of the project, so the project manager has to keep an eye constantly on the physical outcomes of the project. A variant of this is the so-called ‘outsourced supply team’, which simply means that the team is physically situated remotely from the project manager, who then encounters the additional problem of ‘managing at a distance’.
Mixed structures
Teams often have mixed structures:
- Some members may be employed to work full time on the project and be fully responsible to the project manager. Project managers themselves are usually employed full time.
- Others may work part time, and be responsible to the project manager only during their time on the project. For example, internal staff may well work on several projects at the same time. Alternatively, an external consultant working on a given project may also be involved in a wider portfolio of activities.
- Some may be part of a matrix arrangement, whereby their work on the project is overseen by the project manager and they report to their line manager for other matters. Project administrators often function in this way, serving the project for its duration, but having a career path within a wider administrative service.
- Still others may be part of a functional hierarchy, undertaking work on the project under their line manager’s supervision by negotiation with their project manager. For instance, someone who works in an organization’s legal department may provide the project team with access to legal advice when needed.
In relatively small projects the last two arrangements are a very common way of accessing specialist services that will only be needed from time to time.
Modern teams
In addition to the traditional types of teams or groups outlined above, recent years have seen the growth of interest in three other important types of team: ‘self-managed teams’, ‘self-organizing teams’, and ‘dispersed virtual teams.’
A typical self-managed team may be permanent or temporary. It operates in an informal and non-hierarchical manner, and has considerable responsibility for the way it carries out its tasks. It is often found in organizations that are developing total quality management and quality assurance approaches. The Industrial Society Survey observed that: “Better customer service, more motivated staff, and better quality of output are the three top motives for moving to [self-managed teams], managers report.”
In contrast, organizations that deliberately encourage the formation of self-organizing teams are comparatively rare. Teams of this type can be found in highly flexible, innovative organizations that thrive on creativity and informality. These are modern organizations that recognize the importance of learning and adaptability in ensuring their success and continued survival. However, self-organizing teams exist, unrecognized, in many organizations. For instance, in traditional, bureaucratic organizations, people who need to circumvent the red tape may get together in order to make something happen and, in so doing, spontaneously create a self-organizing team. The team will work together, operating outside the formal structures, until its task is done and then it will disband.
Table 2 shows some typical features of self-managed and self-organizing teams.
Table 2: Comparing Self-managed and Self-Organizing Teams
| Self-managed team | Self-organizing team |
| Usually part of the formal reporting structure | Usually outside the formal reporting structure |
| Members usually selected by management | Members usually self-selected volunteers |
| Informal style of working | Informal style of working |
| Indirectly controlled by senior management | Senior management influences only the team’s boundaries |
| Usually a permanent leader, but may change | Leadership variable – perhaps one, perhaps changing, perhaps shared |
| Empowered by senior management | Empowered by the team members and a supportive culture and environment |
Many organizations set up self-managed or empowered teams as an important way of improving performance and they are often used as a way of introducing a continuous improvement approach. These teams tend to meet regularly to discuss and put forward ideas for improved methods of working or customer service in their areas. Some manufacturers have used multi-skilled self-managed teams to improve manufacturing processes, to enhance worker participation and improve morale. Self-managed teams give employees an opportunity to take a more active role in their working lives and to develop new skills and abilities. This may result in reduced staff turnover and less absenteeism.
Self-organizing teams are usually formed spontaneously in response to an issue, idea or challenge. This may be the challenge of creating a radically new product, or solving a tough production problem. In Japan, the encouragement of self-organizing teams has been used as a way of stimulating discussion and debate about strategic issues so that radical and innovative new strategies emerge. By using a self-organizing team approach companies were able to tap into the collective wisdom and energy of interested and motivated employees.
Following the COVID-19 pandemic, virtual teams are increasingly common. A virtual team is one whose primary means of communicating is electronic, with only occasional phone and face-to-face communication, if at all. Virtual teams use technologies like, Zoom, Skype, Teams, Basecamp, etc. to coordinate, meet, and share work (Kniffen et al., 2021). Table 3 contains a summary of benefits virtual groups provide to organizations and individuals, as well as the potential challenges and disadvantages virtual groups present.
Table 3. Teams have organizational and individual benefits, as well as possible challenges and disadvantages
| The Organization Benefits | The Individual Benefits | Possible Challenges and Disadvantages |
| People can be hired with the skills and competences needed regardless of location | People can work from anywhere at any time | Communicating effectively across distances |
| In some cases, working across different time zones can extend the working day | Physical location is not a recruitment issue; relocation is unnecessary | Management lacks the planning necessary for a virtual group |
| It can enable products to be developed more quickly | Travel expenses and commuting time are cut | Technology is complicated and/or unfamiliar to some or all members |
| Expenses associated with travel and relocation can be cut; Carbon emissions can be reduced. | People can work from anywhere at any time | Difficult to coordinate times and hard to squeeze all the information into a more narrow time slot |
Why do (only some) teams succeed?
Clearly, there are no hard-and-fast rules which lead to team effectiveness. The determinants of a successful team are complex and not equivalent to following a set of prescriptions. However, the results of poor teamwork can be expensive, so it is useful to draw on research, experience and case studies to explore some general guidelines. What do I mean by ‘team effectiveness’? – the achievement of goals alone? Where do the achievements of individual members fit in? and How does team member satisfaction contribute to team effectiveness?
Borrowing from Adair’s (1983) leadership model, the left-hand side of Figure 3 shows the main constituents of team effectiveness: the satisfaction of individual membership needs, successful team interaction and the achievement of team tasks. These elements are not discrete, so Figure 3 shows them as overlapping. For example, team member satisfaction will be derived not only from the achievement of tasks but also from the quality of team relationships and the more social aspects of teamworking: people who work almost entirely on their own, such as teleworkers and self-employed business owner-managers, often miss the opportunity to bounce ideas off colleagues in team situations. The experience of solitude in their work can, over time, create a sense of isolation, and impair their performance. The effectiveness of a team should also relate to the next step, to what happens after the achievement of team goals.
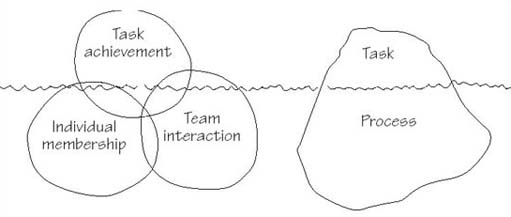
The three elements could be reconfigured as an iceberg, most of which is below the water’s surface (the right-hand side of Figure 3). Superficial observation of teams in organizations might suggest that most, if not all, energy is devoted to the explicit task (what is to be achieved, by when, with what budget and what resources). Naturally, this is important. But too often the concealed part of the iceberg (how the team will work together) is neglected. As with real icebergs, shipwrecks can ensue.
For instance, if working in a particular team leaves its members antagonistic towards each other and disenchanted with the organization to the point of looking for new jobs, then it can hardly be regarded as fully effective, even if it achieves its goals. The measure of team effectiveness could be how well the team has prepared its members for the transition to new projects, and whether the members would relish the thought of working with each other again.
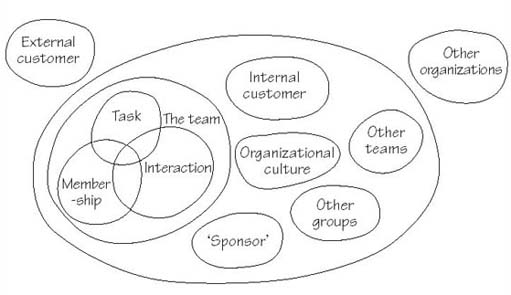
In addition to what happens inside a team there are external influences that impact upon team operations. Restated, teams operate in complex systems composed on both internal and external stakeholders, resources, and outcomes. The factors shown in Figure 4 interact with each other in ways that affect the team and its development. We don’t fully understand the complexity of these interactions and combinations. The best that we can do is discuss each factor in turn and consider some of the interactions between them and how they relate to team effectiveness. For instance, discussions about whether the wider culture of an organization supports and rewards teamworking, whether a team’s internal and/or external customers clearly specify their requirements and whether the expectations of a team match those of its sponsor will all either help or hinder a team’s ongoing vitality.
References
- Adair, J. (1983) Effective Leadership, Gower.
- Industrial Society (1995) Managing Best Practice: Self Managed Teams. Publication no. 11, May 1995, London, Industrial Society.
- Kniffin, K. M., Narayanan, J., Anseel, F., Antonakis, J., Ashford, S. P., Bakker, A. B., … & Vugt, M. V. (2021). COVID-19 and the workplace: Implications, issues, and insights for future research and action. American Psychologist, 76(1), 63.
- Makin, P., Cooper, C. and Cox, C. (1989) Managing People at Work, The British Psychological Society and Routledge.
- Stanton, A. (1992). Learning from experience of collective teamwork. In Paton R., Cornforth C, and Batsleer, J. (Eds.) Issues in Voluntary and Non-profit Management, pp. 95–103, Addison-Wesley.
- Piercy, C. W., & Kramer, M. W. (2017). Exploring dialectical tensions of leading volunteers in two community choirs. Communication Studies, 68, 208-226.
Groups used to organize and distribute work, pool information, devise plans, coordinate activities, increase commitment, negotiate, resolve conflicts and conduct inquests.
Groups not formally sanctioned (by an organization) which serve to satisfy needs of affiliation, and act as a forum for exploring self-concept as a means of gaining support, and so on.
a particularly cohesive and purposeful type of work group
the less obvious and more complex the task to be addressed
the number of people each manager or supervisor is directly responsible for
a group of people who come together as a distinct organizational unit in order to work on a project or projects.
other parties involved or affected by decision a team makes (e.g., customers, co-workers, managers, etc.)
a team in which members report to different managers for different aspects of their work
A team brought in from outside in order to do the project work
A team which operates in an informal and non-hierarchical manner, and has considerable responsibility for the way it carries out its tasks
A team in which members self-select their membership, this type of team is typically marked by an informal work style and little input or direction from senior management. These teams are often formed spontaneously in response to an issue, idea or challenge.
A combination of task achievement, individual success, and positive team interactions across both the task and process dimensions of team work.
A system is a group of interacting or interrelated elements that interact to form a unified whole. A system is surrounded and influenced by its environment. Systems are described by its boundaries, structure and purpose and expressed in its functioning.

