Arguments and Information
5
Learning Objectives
- Define what an argument is
- Introduce ethos, pathos, and logos
- Identify the argument structure of claim, evidence, and warrant
- Explore effective language
You may be wondering, “What exactly is an argument? Haven’t I already decided on my main argument and topic?”
An argument is a series of statements in support of a claim, assertion, or proposition. So far, we’ve discussed thesis statements as the main argumentative through-line for a speech—it’s what you want to inform, persuade, or entertain the audience about.
Your thesis statement, however, is just one component of an argument, i.e. “here’s what I want to inform you about / persuade you to consider.” It is the main claim of your speech. Your task is to prove the reliability of that claim (with evidence) and demonstrate, through the body of the speech, how or why that information should matter to the audience. In this chapter, we will fill in the other structural components of an argument to make sure that your thesis statement has adequate support and proof. We’ll also outline the importance of language and tips to guarantee that your language increases the effective presentation of your argument.
An Overview of Arguments
It may be tempting to view arguments as only relevant to persuasion or persuasive speeches. After all, we commonly think of arguments as occurring between different perspectives or viewpoints with the goal of changing someone’s mind. Arguments are important when persuading (and we will re-visit persuasive arguments in Chapter 13), but you should have clear evidence and explanations for any type of information sharing.
All speech types require proof to demonstrate the reliability of their claims. Remember, when you speak, you are being an advocate and selecting information that you find relevant to your audience, so arguments are necessary to, at a bare minimum, build in details about the topic’s importance.
With speeches that primarily inform, a sound argument demonstrates the relevance and significance of the topic for your audience. In other words, “this is important information because…” or “here’s why you should care about this.” If you are giving a ceremonial speech, you should provide examples of your insights. In a speech of introduction, for example, you may claim that the speaker has expertise, but you should also provide evidence of their previous accomplishments and demonstrate why those accomplishments are significant.
For each speech type, a well-crafted speech will have multiple arguments throughout. Yes, your thesis statement is central to speech, and your content should be crafted around that idea – you will use your entire speech to prove the reliability of that statement. You will also have internal arguments, i.e. your speech’s main points or the “meat” of your speech.
All speech types require arguments, and all arguments use the rhetorical appeals of ethos, pathos, and logos to elicit a particular feeling or response from your audience.
Ethos, or establishing your credibility as a speaker, is necessary for any speech. If you’re informing the audience about a key topic, they need to know that you’re a trustworthy and reliable speaker. A key way to prove that credibility is through crafting arguments that are equally credible. Using reliable and well-tested evidence is one way to establish ethos.
Using reason or logic, otherwise known as logos, is also a key rhetorical appeal. By using logos, you can select logical evidence that is well-reasoned, particularly when you’re informing or persuading. We’ll talk more about logic and fallacies (to avoid) in Chapter 13.
Pathos, or emotional appeals, allows you to embed evidence or explanations that pull on your audience’s heartstrings or other feelings and values. Pathos is common in ceremonial speeches, particularly speeches that eulogize or celebrate a special occasion.
All three rhetorical appeals are important mechanisms to motivate your audience to listen or act. All three should be done ethically (see Chapter 1) and with the speech context and audience in mind.
Regardless of which rhetorical proof you use, your arguments should be well-researched and well-structured. Below, we explore the structure of an argument in more detail.
The Structure: Claim, Evidence, Warrant
Arguments have the following basic structure (see Figure 5.1):
- Claim: the main proposition crafted as a declarative statement.
- Evidence: the support or proof for the claim.
- Warrant: the connection between the evidence and the claim.
Each component of the structure is necessary to formulate a compelling argument.
The Toulmin Model
British Philosopher, Stephen Toulmin, created the “Toulmin Model” – a model that describes the structure of an argument or method of reasoning. Claim, evidence, and warrant are, if done well, necessary to create a good argument (O’Connor, 1958).
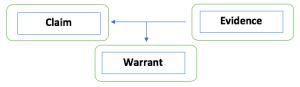
Evidence and warrants are the specifics that make your ideas, arguments, assertions, points, or concepts real and concrete by relating the information to your audience. Not all audiences are compelled by the same evidence, for example, so creating a well-structured argument also means being responsive to audiences.
Consider going to lunch with a friend. Your friend suggests a restaurant that you have not heard of, so you request some additional information, proof, or evidence of their choice. We could map the argument like this:
- Claim: “Let’s go to Jack’s Shack for lunch.”
- Evidence: “I have been there a few times and they have good servers.”
So far, your friend is highlighting service as the evidence to support their claim that Jack’s Shack is a good choice for lunch. However, the warrant is still missing. For a warrant, they need to demonstrate why good service is sufficient proof to support their claim. Remember that the warrant is the connection. For example:
- Warrant: “You were a server, so I know that you really appreciate good service. I have never had a bad experience at Jack’s Shack, so I am confident that it’s a good lunch choice for both of us.”
In this case, they do a good job of both connecting the evidence to the claim and connecting the argument to their audience – you! They have selected evidence based on your previous experience as a server (likely in hopes to win you over to their claim!).
Using “claim, evidence, and warrant” can assist you in verifying that all parts of the argumentative structure are present. Below, we dive deeper into each category.
Claims
A claim is a declarative statement or assertion—it is something that you want your audience to accept or know. Like we’ve mentioned, your thesis statement is a key claim in your speech because it’s the main argument that you’re asking the audience to consider.
Different claims serve different purposes. Depending on the purpose of the argument, claims can be factual, opinionated, or informative. Some claims, for example, may be overtly persuading the audience to change their mind about a controversial issue, i.e. “you should support this local policy initiative.”
Alternatively, a claim may develop the significance of a topic (i.e. “this is why you should care about this information”) or highlight a key informative component about a person, place, or thing (“Hillary Clinton had an intriguing upbringing”). You might, for example, write a speech that informs the audience about college textbook affordability. Your working thesis might read, “Universities are developing textbook affordability initiatives.” Your next step would be to develop main points and locate evidence that supports your claim.
It’s important to develop confidence around writing and identifying your claims. Identifying your main ideas will allow you to then identify evidence in support of those declarative statements. If you aren’t confident about what claims you’re making, it will be difficult to identify the evidence in support of that idea, and your argument won’t be structurally complete. Remember that your thesis statement your main claim, but you likely have claims throughout your speech (like your main points).
Evidence
Evidence is the proof or support for your claim. It answers the question, “how do I know this is true?” With any type of evidence, there are three overarching considerations.
First, is this the most timely and relevant type of support for my claim? If your evidence isn’t timely (or has been disproven), it may drastically influence the credibility of your claim.
Second, is this evidence relatable and clear for my audience? Your audience should be able to understand the evidence, including any references or ideas within your information. Have you ever heard a joke or insight about a television show that you’ve never seen? If so, understanding the joke can be difficult. The same is true for your audience, so stay focused on their knowledge base and level of understanding.
Third, did I cherry-pick? Avoid cherry-picking evidence to support your claims. While we’ve discussed claims first, it’s important to arrive at a claim after seeing all the evidence (i.e. doing the research). Rather than finding evidence to fit your idea (cherry-picking), the evidence should help you arrive at the appropriate claim. Cherry-picking evidence can reduce your ethos and weakened your argument.
With these insights in mind, we will introduce you to five evidence types: examples, narratives, facts, statistics, and testimony. Each provides a different type of support, and it’s suggested that you integrate a variety of different evidence types. Understanding the different types of evidence will assist as you work to structure arguments and select support that best fits the goal of your speech.
Examples
Examples are specific instances that illuminate a concept. They are designed to give audiences a reference point. An example must be quickly understandable—something the audience can pull out of their memory or experience quickly.
Evidence by example would look like this:
Claim: Textbook affordability initiatives are assisting universities in implementing reputable, affordable textbooks.
Evidence: Ohio has implemented a textbook affordability initiative, the Open Ed Collaborative, to alleviate the financial strain for students (Jaggers, Rivera, Akani, 2019).
Ohio’s affordability initiative functions as evidence by example. This example assists in demonstrating that such initiatives have been successfully implemented. Without providing an example, your audience may be skeptical about the feasibility of your claim.
Examples can be drawn directly from experience, i.e. this is a real example, or an example can be hypothetical where audiences are asked to consider potential scenarios.
Narratives
Narratives are stories that clarify, dramatize, and emphasize ideas. They have, if done well, strong emotional power (or pathos). While there is no universal type of narrative, a good story often draws the audience in by identifying characters and resolving a plot issue. Narratives can be personal or historical.
Person narratives are powerful tools to relate to your audience and embed a story about your experience with the topic. As evidence, they allow you to say, “I experienced or saw this thing first hand.” As the speaker, using your own experience as evidence can draw the audience in and help them understand why you’re invested in the topic. Of course, personal narratives must be true. Telling an untrue personal narrative may negatively influence your ethos for an audience.
Historical narratives (sometimes called documented narratives) are stories about a past person, place, or thing. They have power because they can prove and clarify an idea by using a common form— the story. By “historical” we do not mean that the story refers to something that happened many years ago, only that it has happened in the past and there were witnesses to validate the happening. Historical narratives are common in informative speeches.
Facts
Facts are observations, verified by multiple credible sources, that are true or false. The National Center for Science Education (2008) defines fact as:
an observation that has been repeatedly confirmed an . . . is accepted as ‘true.’ Truth in science, however, is never final and what is accepted as a fact today may be modified or even discarded tomorrow.
“The sun is a star” is an example of a fact. It’s been observed and verified based on current scientific understanding and categorization; however, future technology may update or disprove that fact.
In our modern information age, we recommend “fact-checking a fact” because misinformation can be presented as truth. This means verifying all facts through credible research (check back to Chapter 4 on research). Avoid taking factual information for granted and make sure that the evidence comes from reputable sources that are up-to-date.
Statistics
Statistics are the collection, analysis, comparison, and interpretation of numerical data. As evidence, they are useful in summarizing complex information, quantifying, or making comparisons. Statistics are powerful pieces of evidence because numbers appear straightforward. Numbers provide evidence that quantifies, and statistics can be helpful to clarify a concept or highlighting the depth of a problem.
You may be wondering, “What does this actually mean?” (excuse our statistical humor). We often know a statistic when we find one, but it can be tricky to understand how a statistic was derived.
Averages and percentages are two common deployments of statistical evidence.
An “average” can be statistically misleading, but it often refers to the mean of a data set. You can determine the mean (or average) by adding up the figures and dividing by the number of figures present. If you’re giving a speech on climate change, you might note that, in 2015, the average summer temperature was 97 degrees while, in 1985, it was just 92 degrees.
When using statistics, comparisons can help translate the statistic for an audience. In the example above, 97 degrees may seem hot, but the audience has nothing to compare that statistic to. The 30-year comparison assists in demonstrating a change in temperature.
A percentage expresses a proportion of out 100. For example, you might argue that “textbook costs have risen more than 1000% since 1977” (Popken, 2015). By using a statistical percentage, 1000% sounds pretty substantial. It may be important, however, to accompany your percentage with a comparison to assist the audience in understanding that “This is 3 times higher than the normal rate of inflation” (UTA Libraries). You might also clarify that “college textbooks have risen more than any other college-related cost” (Bureau of Labor Statistics, 2016).
You are responsible for the statistical information that you deploy. It’s all too common for us as information consumers to grab a quick statistic that sounds appealing, but that information may not be reliable.
Be aware of three major statistical issues: small samples, unrepresentative samples, and correlation as causation. In a small sample, an argument is being made from too few examples. In unrepresentative sample, a conclusion is based on surveys of people who do not represent, or resemble, the ones to whom the conclusion is being applied. Finally, it’s common to conflate correlation as causation. In statistics, a correlation refers to the relationship between two variables while causation means that one variable resulted from the other. Be careful not to assume that a correlation means that something has caused the second.
A few other statistical tips:
- Use statistics as support, not as a main point. The audience may cringe or tune you out for saying, “Now I’d like to give you some statistics about the problem of gangs in our part of the state.” That sounds as exciting as reading the telephone book! Use the statistics to support an argument.
- In regard to sources, depend on the reliable ones. Use Chapter 4 as a guide to criticizing and evaluating credible sources.
- Do not overuse statistics. While there is no hard and fast rule on how many to use, there are other good supporting materials and you would not want to depend on statistics alone. You want to choose the statistics and numerical data that will strengthen your argument the most and drive your point home. Statistics can have emotional power as well as probative value if used sparingly.
- Explain your statistics as needed, but do not make your speech a statistics lesson. If you say, “My blog has 500 subscribers” to a group of people who know little about blogs, that might sound impressive, but is it? You can also provide a story of an individual, and then tie the individual into the statistic. After telling a story of the daily struggles of a young mother with multiple sclerosis, you could follow up with “This is just one story in the 400,000 people who suffer from MS in the United States today, according to National MS Society.”
Testimony
Testimony is the words of others. As evidence, testimony can be valuable to gain insight into an expert or a peer’s opinion, experience, or expertise about a topic. Testimony can provide an audience with a relevant perspective that the speaker isn’t able to provide. We’ll discuss two types of testimony: expert and non-expert.
Expert Testimony
What is an expert? An expert is someone with recognized credentials, knowledge, education, and/or experience in a subject. To quote an expert on expertise, “To be an expert, someone needs to have considerable knowledge on a topic or considerable skill in accomplishing something” (Weinstein, 1993).
A campus bookstore manager could provide necessary testimony on the changing affordability of textbooks over time, for example. As someone working with instructors, students, and publishers, the manager would likely have an insight and a perspective that would be difficult to capture otherwise. They would provide unique and credible evidence.
In using expert testimony, you should follow these guidelines:
- Use the expert’s testimony in their relevant field. A person may have a Nobel Prize in economics, but that does not make them an expert in biology.
- Provide at least some of the expert’s relevant credentials.
- If you interviewed the expert yourself, make that clear in the speech also. “When I spoke with Dr. Mary Thompson, principal of Park Lake High School, on October 12, she informed me that . . .”
Expert testimony is one of your strongest supporting materials to prove your arguments. When integrating their testimony as evidence, make sure their testimony clearly supports your claim (rather than an interesting idea on the topic that is tangential to your assertions).
Non-Expert/Peer Testimony
Any quotation from a friend, family member, or classmate about an incident or topic would be peer testimony. It is useful in helping the audience understand a topic from a personal point of view. For example, you may draw on testimony from a campus student who was unable to afford their campus textbooks. While they may lack formalized expertise in textbook affordability, their testimony might demonstrate how the high cost limited their engagement with the class. Their perspective and insight would be valuable for an audience to hear.
Warrants
The third component of any argument is the warrant. Warrants connect the evidence and the claim. They often answer the question, “what does this mean?” Warrants are an important component of a complete argument because they:
- Highlight the significance of the evidence;
- Detail how the evidence supports the claims;
- Outline the relevance of the claim and evidence to the audience.
For example, consider the claim that “communication studies provide necessary skills to land you a job.” To support that claim, you might locate a statistic and argue that, “The New York Times had a recent article stating that 80% of jobs want good critical thinking and interpersonal skills.” It’s unclear, however, how a communication studies major would prepare someone to fulfill those needs. To complete the argument, you could include a warrant that explains, “communication studies classes facilitate interpersonal skills and work to embed critical thinking activities throughout the curriculum.” You are connecting the job skills (critical thinking) from the evidence to the discipline (communication studies) from your claim.
Despite their importance, warrants are often excluded from arguments. As speechwriters and researchers, we spend lots of time with our information and evidence, and we take for granted what we know. If you are familiar with communication studies, the connection between the New York Times statistic referenced above and the assertion that communication studies provides necessary job skills may seem obvious. For an unfamiliar audience, the warrant provides more explanation and legitimacy to the evidence.
We know what you’re thinking: “Really? Do I always need an explicit warrant?”
It’s true that some warrants are inferred, meaning that we often recognize the underlying warrant without it being explicitly stated. For example, I might say, “The baking time for my cookies was too hot. The cookies burned.” In this statement, I’m claiming that the temperature is too hot and using burnt cookies as the evidence. We could reasonably infer the warrant, i.e. “burnt cookies are a sign that they were in the oven for too long.”
Inferred warrants are common in everyday arguments and conversations; however, in a formal speech, having a clear warrant will increase the clarity of your argument. If you decide that no explicit warrant is needed, it’s still necessary to ask, “what does this argument mean for my thesis? What does it mean for my audience?” Your goal is to keep as many audience members listening as possible, and warrants allow you to think critically about the information that you’re presenting to that audience.
When writing warrants, keep the following insights in mind:
- Avoid exaggerating your evidence, and make sure your warrant honors what the evidence is capable of supporting;
- Center your thesis statement. Remember that your thesis statement, as your main argument, should be the primary focus when you’re explaining and warranting your evidence.
- A good warrant should be crafted with your content and context in mind. As you work on warrants, ask, “why is this claim/evidence important here? For this argument? Now? For this audience?”
- Say it with us: ethos, pathos, and logos! Warrants can help clarify the goal of your argument. What appeal are you using? Can the warrant amplify that appeal?
Now that you have a better understanding of each component of an argument, let’s conclude this section with a few complete examples.
Claim: The Iowa Wildcats will win the championship.
Evidence: In 2019, the National Sporting Association found that the Wildcats had the most consistent and well-rounded coaching staff. Referees of the game agreed, and also praised the players ability for high scoring.
Warrant: Good coaching and high scoring are probable indicators of past champions and, given this year’s findings, the Wildcat’s are on mark to win it all.
Here’s an example with a more general approach to track the potential avenues for evidence:
Claim: Sally Smith will win the presidential election.
Evidence: [select evidence that highlights their probable win, including: they’ve won the most primaries; they won the Iowa caucus; they’re doing well in swing states; they have raised all the money; they have the most organized campaign.”
Warrant: [based on your evidence select, you can warrant why that evidence supports a presidential win].
Using Language Effectively
Claim, evidence, and warrant are useful categories when constructing or identifying a well-reasoned argument. However, a speech is much more than this simple structure over and over (how boring, huh?).
When we craft arguments, it’s tempting to view our audience as logic-seekers who rely solely on rationality, but that’s not true. Instead, Walter Fisher (1984) argues that humans are storytellers, and we make sense of the world through good stories. A good speech integrates argumentative components while telling a compelling story about your argument to the audience. A key piece of that story is how you craft the language—language aids in telling an effective story.
We’ll talk more about language in Chapter 7 (verbal delivery), but there are a few key categories to keep in mind as you construct your argument and story.
Language: What Do We Mean?
Language is any formal system of gestures, signs, sounds, and symbols used or conceived as a means of communicating thought, either through written, enacted, or spoken means. Linguists believe there are far more than 6,900 languages and distinct dialects spoken in the world today (Anderson, 2012). Despite being a formal system, language results in different interpretations and meanings for different audiences.
It is helpful for public speakers to keep this mind, especially regarding denotative and connotative meaning. Wrench, Goding, Johnson, and Attias (2011) use this example to explain the difference:
When we hear or use the word “blue,” we may be referring to a portion of the visual spectrum dominated by energy with a wave-length of roughly 440–490 nanometers. You could also say that the color in question is an equal mixture of both red and green light. While both of these are technically correct ways to interpret the word “blue,” we’re pretty sure that neither of these definitions is how you thought about the word. When hearing the word “blue,” you may have thought of your favorite color, the color of the sky on a spring day, or the color of a really ugly car you saw in the parking lot. When people think about language, there are two different types of meanings that people must be aware of: denotative and connotative. (p. 407)
Denotative meaning is the specific meaning associated with a word. We sometimes refer to denotative meanings as dictionary definitions. The scientific definitions provided above for the word “blue” are examples of definitions that might be found in a dictionary. Connotative meaning is the idea suggested by or associated with a word at a cultural or personal level. In addition to the examples above, the word “blue” can evoke many other ideas:
- State of depression (feeling blue)
- Indication of winning (a blue ribbon)
- Side during the Civil War (blues vs. grays)
- Sudden event (out of the blue)
- States that lean toward the Democratic Party in their voting
- A slang expression for obscenity (blue comedy)
Given these differences, the language you select may have different interpretations and lead to different perspectives. As a speechwriter (and communicator), being aware of different interpretations can allow you select language that is the most effective for your speaking context and audience.
Using Language to Craft Your Argument
Have you ever called someone a “wordsmith?” If so, you’re likely complimenting their masterful application of language. Language is not just something we use; it is part of who we are and how we think. As such, language can assist in clarifying your content and creating an effective message.
Achieve Clarity
Clear language is powerful language. If you are not clear, specific, precise, detailed, and sensory with your language, you won’t have to worry about being emotional or persuasive, because you won’t be understood. The goal of clarity is to reduce abstraction; clarity will allow your audience to more effectively track your argument and insight, especially because they only have one chance to listen.
Concreteness aids clarity. We usually think of concreteness as the opposite of abstraction. Language that evokes many different visual images in the minds of your audience is abstract language. Unfortunately, when abstract language is used, the images evoked might not be the ones you really want to evoke. Instead, work to be concrete, detailed, and specific. “Pity,” for example, is a bit abstract. How might you describe pity by using more concrete words?
Clear descriptions or definitions can aid in concreteness and clarity.
To define means to set limits on something; defining a word is setting limits on what it means, how the audience should think about the word, and/or how you will use it. We know there are denotative and connotative definitions or meanings for words, which we usually think of as objective and subjective responses to words. You only need to define words that would be unfamiliar to the audience or words that you want to use in a specialized way.
Describing is also helpful in clarifying abstraction. The key to description is to think in terms of the five senses: sight (visual: how does the thing look in terms of color, size, shape); hearing (auditory: volume, musical qualities); taste (gustatory: sweet, bitter, salty, sour, gritty, smooth, chewy); smell (olfactory: sweet, rancid, fragrant, aromatic, musky); and feel (tactile: rough, silky, nubby, scratchy).
If you were, for example, talking about your dog, concrete and detailed language could assist in “bring your dog to life,” so to speak, in the moment.

- Boring and abstract: My dog is pretty great. He is well behaved, cute, and is friendly to all of our neighbors. I get a lot of compliments about him, and I really enjoy hanging out with him outside in the summer.
- Concrete and descriptive: Buckley, my golden-brown Sharpei mix, is a one-of-a-kind hound. Through positive treat reinforcement, he learned to sit, shake, and lay down within one month. He will also give kisses with his large and wrinkly snout. He greats passing neighbors with a smile and enjoys Midwest sunbathing on our back deck in the 70-degree heat.
Doesn’t the second description do Image 5.2 more justice? Being concrete and descriptive paints a picture for the audience and can increase your warrant’s efficacy. Being descriptive, however, doesn’t mean adding more words. In fact, you should aim to “reduce language clutter.” Your descriptions should still be purposeful and important.
Be Effective
Language achieves effectiveness by communicating the right message to the audience. Clarity contributes to effectiveness, but effectiveness also includes using familiar and interesting language.
Familiar language is language that your audience is accustomed to hearing and experiencing. Different communities and audience use language differently. If you are part of an organization, team, or volunteer group, there may be language that is specific and commonly used in those circles. We call that language jargon, or specific, technical language that is used in a given community. If you were speaking to that community, drawing on those references would be appropriate because they would be familiar to that audience. For other audiences, drawing on jargon would be ineffective and either fail to communicate an idea to the audience or implicitly community that you haven’t translated your message well (reducing your ethos).
In addition to using familiar language, draw on language that’s accurate and interesting. This is difficult, we’ll admit it! But in a speech, your words are a key component of keeping the audience motivated to listen, so interesting language can peak and maintain audience interest.
Active language is interesting language. Active voice, when the subject in a sentence performs the action, can assist in having active and engaging word choices. An active sentence would read, “humans caused climate change” as opposed to a passive approach of, “climate change was caused by humans.” Place subjects at the forefront. A helpful resource on active voice can be found here.
You must, however, be reflexive in the language process.
Practicing Reflexivity
Language reflects our beliefs, attitudes, and values – words are the mechanism we use to communicate our ideas or insights. As we learned in Chapter 1, communication both creates and is created by culture. When we select language, we are also representing and creating ideas and cultures – language has a lot of power.
To that end, language should be a means of inclusion and identification, rather than exclusion.
You might be thinking, “Well I am always inclusive in my language,” or “I’d never intentionally use language that’s not inclusive.” We understand, but intention is less important than effect.
Consider the term “millennial”— a categorization that refers to a particular age group. It can be useful to categorize different generations, particularly from a historical and contemporary perspective. However, people often argue that “millennials are the laziest generation” or “millennials don’t know hard work!” In these examples, the intention may be descriptive, but they are selecting language that perpetuates unfair and biased assumptions about millions of people. The language is disempowering (and the evidence, when present, is weak).
Language assists us in categorizing or understanding different cultures, ideas, or people; we rely on language to sort information and differentiate ourselves. In turn, language influences our perceptions, even in unconscious and biased ways.
The key is to practice reflexivity about language choices. Language isn’t perfect, so thinking reflexively about language will take time and practice.
For example, if you were crafting a hypothetical example about an experience in health care, you might open with a hypothetical example: “Imagine sitting for hours in the waiting room with no relief. Fidgeting and in pain, you feel hopeless and forgotten within the system. Finally, you’re greeted by the doctor and he escorts you to a procedure room.” It’s a great story and there is vivid and clear language. But are there any changes that you’d make to the language used?
Remember that this is a hypothetical example. Using reflexive thinking, we might question the use of “he” to describe the doctor. Are there doctors that are a “he”? Certainly. Are all doctors a “he”? Certainly not. It’s important to question how “he” gets generalized to stand-in for doctors or how we may assume that all credible doctors are men.
Practicing reflexivity means questioning the assumptions present in our language choices (like policemen rather than police officers). Continue to be conscious of what language you draw on to describe certain people, places, or ideas. If you aren’t sure what language choices are best to describe a group, ask; listen; and don’t assume.
Conclusion
In this chapter, we discussed crafting complete, well-reasoned arguments. Claim, evidence, and warrant are helpful structural components when crafting arguments. Use Chapter 4 to aid in research that will enable you to locate the best evidence for each claim within your speech.
Remember, too, that language plays a central role in telling a compelling story. Up next: organizing and outlining.
Media Attributions
- Sharpei-Mix © Mapes

